This chapter was very detailed about graphics and pictures. I learned a lot about how images go from paper onto the screen. There is a lot involved with getting these images onto the screen and to make them look real. A graphic is any type of visual presentation that can be displayed on a physical surface such as a sheet of paper, wall, poster, blackboard, or computer monitor. They are products of a human imagination. They can be created by hand or with computer assisted drawing or design tools.
Images are a two- or three-dimensional representation of a person, animal, object, or scene in the natural world. Digital media is used by cameras. The resolution is the image quality of a raster image and refers to the size and quantity of the pixels the image contains.

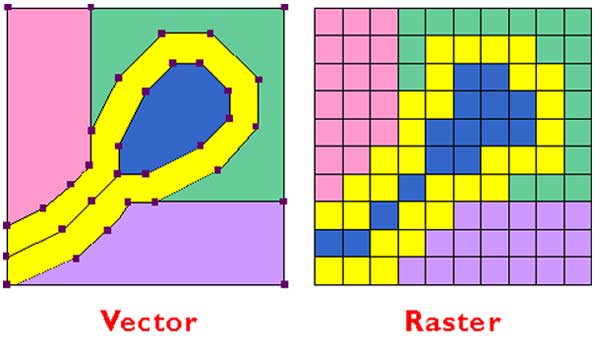
Like the tiny bits of tile, a pixel is the smallest deniable element of a raster image. Editors usually measure graphics in pixels, and pixel counts and density determine the physical size and quality of an image. Pixel count is the total number of pixels in a raster matrix. To determine the pixel count, multiply the horizontal and vertical pixel dimensions.

Raster images have different formats. GIF- offers 256 colors and transparency and is a lossless compression format. Examples would be logos and other images with lines and solid blocks of color. JPEG- offers 16.8 million colors but does not support transparency. It is a glossy compression format and is used for photographs. PNG offers 16.8 million colors and transparency, but you can choose to use fewer colors to save file space. These can be very small and older web browsers do not support this.
Vector images defines the area of a picture using paths, made up of points, lines, curves, shapes. Each vector forms the outline of a geometric region containing color information. Paths can be mathematically resized; vector graphics can be scaled up or down without losing picture clarity. Clip-art and typefaces are examples of vector graphics.
Interlaced scanning is something early television standards adopted as a method of rater scanning. This is called interlaced scanning to minimize both bandwidths use and flickering. Fields are one complete scanning pass of either the odd or even scan lines.
Digital television offers many advantages over legacy analog formats. Content created for digital media is more fluid: it can b easily re-purposed and distrusted through secondary channels of communication, making DTV more compatible with computer and internet based systems and services. DTV also, offers less signal interference and uses less bandwidth than equivalent analog television broadcast, which is an advantage because the amount of broadcast is finite.
